About Chronic Care disease
Chronic care management involves a personalized, multidisciplinary approach focused on regular monitoring, preventive care, education, lifestyle modifications, and therapeutic interventions aimed at enhancing the patient’s quality of life and reducing the risk of complications associated with these chronic health conditions. Regular communication and collaboration between patients, caregivers, healthcare providers, and specialists play a pivotal role in achieving successful chronic care management.
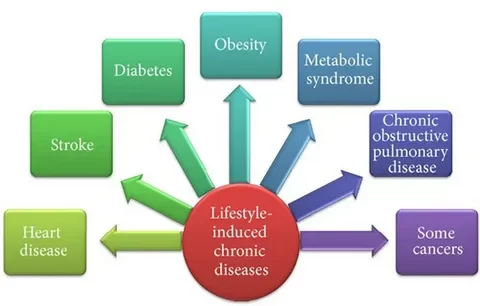
Hypertension: Or high blood pressure, necessitates ongoing management through regular check-ups, medication adherence, lifestyle changes (like reducing salt intake and exercising), and monitoring to prevent complications like heart attacks and strokes.
Diabetes Mellitus: Requires comprehensive care involving blood sugar monitoring, medication management (insulin or oral medications), dietary modifications, exercise routines, and education on foot care and eye health to prevent complications like nerve damage, blindness, or kidney disease.
Chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD): Such as chronic bronchitis or emphysema, demands ongoing care focused on smoking cessation, medication management, pulmonary rehabilitation, breathing exercises, and regular monitoring to alleviate symptoms and prevent exacerbations.
Stroke: Survivors require ongoing care that includes rehabilitation, medication adherence (such as blood thinners or blood pressure medications), physical therapy, speech therapy, and lifestyle adjustments to reduce the risk of recurrent strokes and improve functional abilities.
Metabolic syndrome: A cluster of conditions like obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels, necessitates a multifaceted approach involving weight management, dietary changes, exercise routines, and medication management to reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
Hypertension: Or high blood pressure, necessitates ongoing management through regular check-ups, medication adherence, lifestyle changes (like reducing salt intake and exercising), and monitoring to prevent complications like heart attacks and strokes.
Diabetes Mellitus: Requires comprehensive care involving blood sugar monitoring, medication management (insulin or oral medications), dietary modifications, exercise routines, and education on foot care and eye health to prevent complications like nerve damage, blindness, or kidney disease.
Chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD): Such as chronic bronchitis or emphysema, demands ongoing care focused on smoking cessation, medication management, pulmonary rehabilitation, breathing exercises, and regular monitoring to alleviate symptoms and prevent exacerbations.
Stroke: Survivors require ongoing care that includes rehabilitation, medication adherence (such as blood thinners or blood pressure medications), physical therapy, speech therapy, and lifestyle adjustments to reduce the risk of recurrent strokes and improve functional abilities.
Metabolic syndrome: A cluster of conditions like obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels, necessitates a multifaceted approach involving weight management, dietary changes, exercise routines, and medication management to reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
